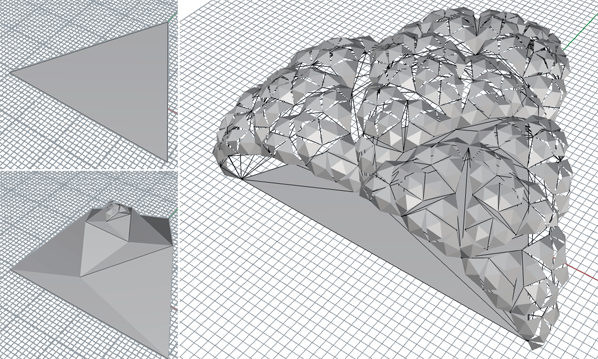
17 Jul Recursive triangulation in RhinoPython
This recursive scripts generates a tree-like structure based on a simple algorithm. Each branch creates four sub-branches in the next level, making it very easy to multiply geometry in an exponential manner. Be careful as it does not provide sufficient error-checking, it simply assumes that you input the correct geometry.
#brocoli subdivision
#script written by Adolfo Nadal
#import libraries
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rss
import random
tmpSrfList = []
#define our function
def subdivideTriaSurf(srf,delete,scFactor):
#duplicate border->returns a list
#in this case we know we only want to have the first object [0]
polyBorderList = rss.DuplicateSurfaceBorder(srf,1)
polyBorder = polyBorderList[0]
#test
print (polyBorder)
#get segments from the border as individual curves (helps get the middle points)
segments = rss.ExplodeCurves(polyBorder)
segment1 = segments[0]
segment2 = segments[1]
segment3 = segments[2]
len = rss.CurveLength(segment1)
#calculate middle points
midPt1 = rss.CurveMidPoint(segment1)
midPt2 = rss.CurveMidPoint(segment2)
midPt3 = rss.CurveMidPoint(segment3)
#calculate vertex
vertexPts = rss.CurvePoints(polyBorder)
pt1 = vertexPts[0]
pt2 = vertexPts[1]
pt3 = vertexPts[2]
#calculate normal vector
normVec = rss.SurfaceNormal(srf,(0,0))
#scaleSurfaceNormal BEFORE ADDING
normVec = rss.VectorScale(normVec,len*scFactor)
#since normal vector is BY DEFAULT 0-based, we add it to the midPoints
#to obtain the normals
midPt1N = rss.VectorAdd(normVec,midPt1)
midPt2N = rss.VectorAdd(normVec,midPt2)
midPt3N = rss.VectorAdd(normVec,midPt3)
“””
rss.AddPoint(midPt1N)
rss.AddPoint(midPt2N)
rss.AddPoint(midPt3N)
“””
#add surfaces to the model
baseSrf = rss.AddSrfPt((midPt1N,midPt2N,midPt3N))
triaSrf1 = rss.AddSrfPt((pt1,midPt1N,midPt3N))
triaSrf2 = rss.AddSrfPt((pt2,midPt2N,midPt1N))
triaSrf3 = rss.AddSrfPt((pt3,midPt3N,midPt2N))
#add control for further subdivision
if(len>5):
subdivideTriaSurf(baseSrf,delete,scFactor)
subdivideTriaSurf(triaSrf1,delete,scFactor)
subdivideTriaSurf(triaSrf2,delete,scFactor)
subdivideTriaSurf(triaSrf3,delete,scFactor)
tmpSrfList.append(baseSrf)
tmpSrfList.append(triaSrf1)
tmpSrfList.append(triaSrf2)
tmpSrfList.append(triaSrf3)
if(delete==”Yes”):
rss.DeleteObjects((baseSrf,triaSrf1,triaSrf2,triaSrf3))
rss.DeleteObject(polyBorder)
#obtain geometry
userSrf = rss.GetObject(“Please select your surface AND make sure that it needs to be defined by 3 points”,8)
#obtain other variables
userDelete = rss.GetString(“Do you want to delete the temp surfaces?, you can alway s do it later”,None,(“Yes”,”No”))
print userDelete
scaleFactor = rss.GetReal(“Please enter non-zero scale factor”,0.25,0.1,5)
#call the function
subdivideTriaSurf(userSrf,userDelete,scaleFactor)
#ask the user to erase temp surfaces
if (userDelete==”No”):
userDeleteAfter = rss.GetString(“Do you want to delete the temp surfaces?”,None,(“Yes”,”No”))
if(userDeleteAfter ==”Yes”):
rss.DeleteObjects(tmpSrfList)












No Comments